Anatomy
 Externally from the front of the iliac crest, a strong tendon (Tensor Fascia Lata) attaches to another tendon (Tractus Iliotibialis) that attaches to the outside of the upper part of the tibia. Several muscles of the thigh attach to the Tractus Iliotibialis. The ligament runs tightly across the outer femoral protuberance (greater trochanter)
Externally from the front of the iliac crest, a strong tendon (Tensor Fascia Lata) attaches to another tendon (Tractus Iliotibialis) that attaches to the outside of the upper part of the tibia. Several muscles of the thigh attach to the Tractus Iliotibialis. The ligament runs tightly across the outer femoral protuberance (greater trochanter)
Thighs from behind:
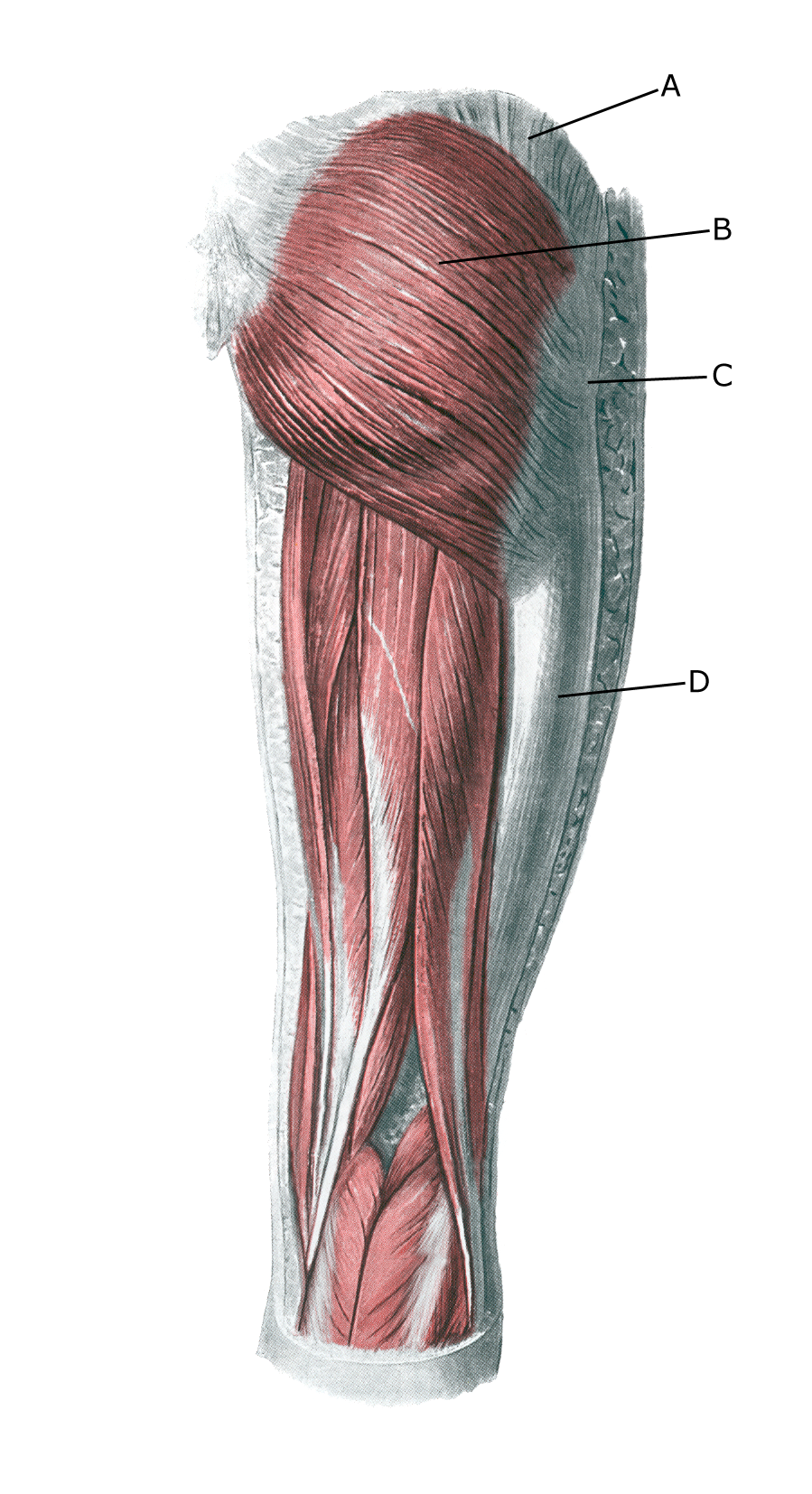
A M. gluteus medius
B. M. gluteus maximus
C. Trochanter major
D.Tractus iliotibialis
Cause
With repetitive movements of the knee and hip joint (running, dancing, gymnastics), the strong ligament (tractus iliotibialis) slides over the outer femoral protuberance (trochanter major), which can cause ‘inflammation’ in the tendon or the underlying bursa. When the inflamed tendon slides over the bony prominence, you may feel a sudden, popping, uncomfortable sensation.
There are at least 3 different causes of jumping hips: external (iliotibial tract), internal (iliopsoas tendon) and joint (intra-articular) causes (Musick SR, Varacallo M. 2023).
Symptoms
Pain on the outside of the hip, sometimes radiating to the outside of the thigh. With certain movements of the hip joint, a clear, sharp, unpleasant clicking sensation can suddenly appear on the outside of the thigh and can often be heard.
Examination
Usually the diagnosis can be made during a general medical examination. Often you can prevent the tendon from slipping over the outer femoral protuberance by holding the tendon aside while performing the provocative movements. The pain will subside in about an hour by injecting a local anaesthetic (diagnostic blockade) around the outer hip protrusion.
If the diagnosis does not seem certain, an ultrasound scan is recommended where the tendon can be seen to slip over the greater trochanter when moving the hip joint
Treatment
Treatment primarily includes relief from pain-inducing activity, stretching and graduated rehabilitation within the pain threshold. If no progress is made despite regular rehabilitation, rehabilitation may be supplemented with medical treatment in the form of arthritis pills (NSAIDs) or adrenal cortical hormone injections.
In severe cases where offloading, proper rehabilitation and medical treatment are ineffective, surgical treatment can be attempted (Walker P, et al. 2021).
Complications
If no progress is made, you need to consider whether the diagnosis is correct. It will often require additional examinations (X-ray, ultrasound or MRI scan).
In particular, the following should be considered:
