Anatomy
Knoglerne i knæleddet omfatter lårbenet (femur), skinnebenet (tibia) og knæskallen (patella). Derudover dannes der et lille led mellem skinnebenet og lægbenet (fibula).
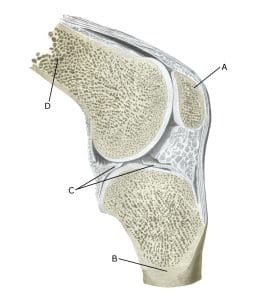 Knee joint:
Knee joint:
A. Patella (Kneecap)
B. Tibiae (Shinbone)
C. Meniscus lateralis (Outer meniscus)
D. Femur (Femur)
Cause of the problem
Bone fractures usually occur after a direct blow or forceful twist.
Symptoms
Sudden onset of pain that worsens with pressure and strain. The symptoms depend on which bone is broken. For example, in cases where the kneecap breaks across the kneecap, the extension function of the knee will be cancelled.
Examination
If you suspect a bone fracture, you should see a doctor (emergency room) immediately for a diagnosis, which is confirmed by an X-ray examination.
Treatment
Treatment is entirely dependent on the type of fracture (offloading, bandaging, surgery)
Rehabilitation, specific:
Rehabilitation is entirely dependent on the type of fracture and should therefore be carried out under the guidance of the treating physician. Attempts should be made to preserve muscle strength in the thigh and shin and maintain mobility in the knee joint as much as possible.
Complications
If it doesn’t progress smoothly, you should be re-evaluated by a doctor to ensure that the fracture is healing as planned.
Especially
As there is a risk that the fracture may cause permanent damage, you should consider reporting it to your insurance company. Especially if there are fractures in the articular surfaces, the risk of long-term consequences is significant.
