Anatomy
The large anterior thigh muscle (musculus quadriceps femoris) consists of four muscles (m vastus lateralis, m vastus medialis, m vastus intermedius and m rectus femoris). The muscles all attach to the top edge of the kneecap. The patella tendon (ligamentum patellae) connects the lower edge of the patella to the upper, anterior part of the tibia (tuberositas tibiae). The knee joint is stabilised by an external (lateral) and internal (medial) ligament and the patella is stabilised by various ligaments between the patella and femur.
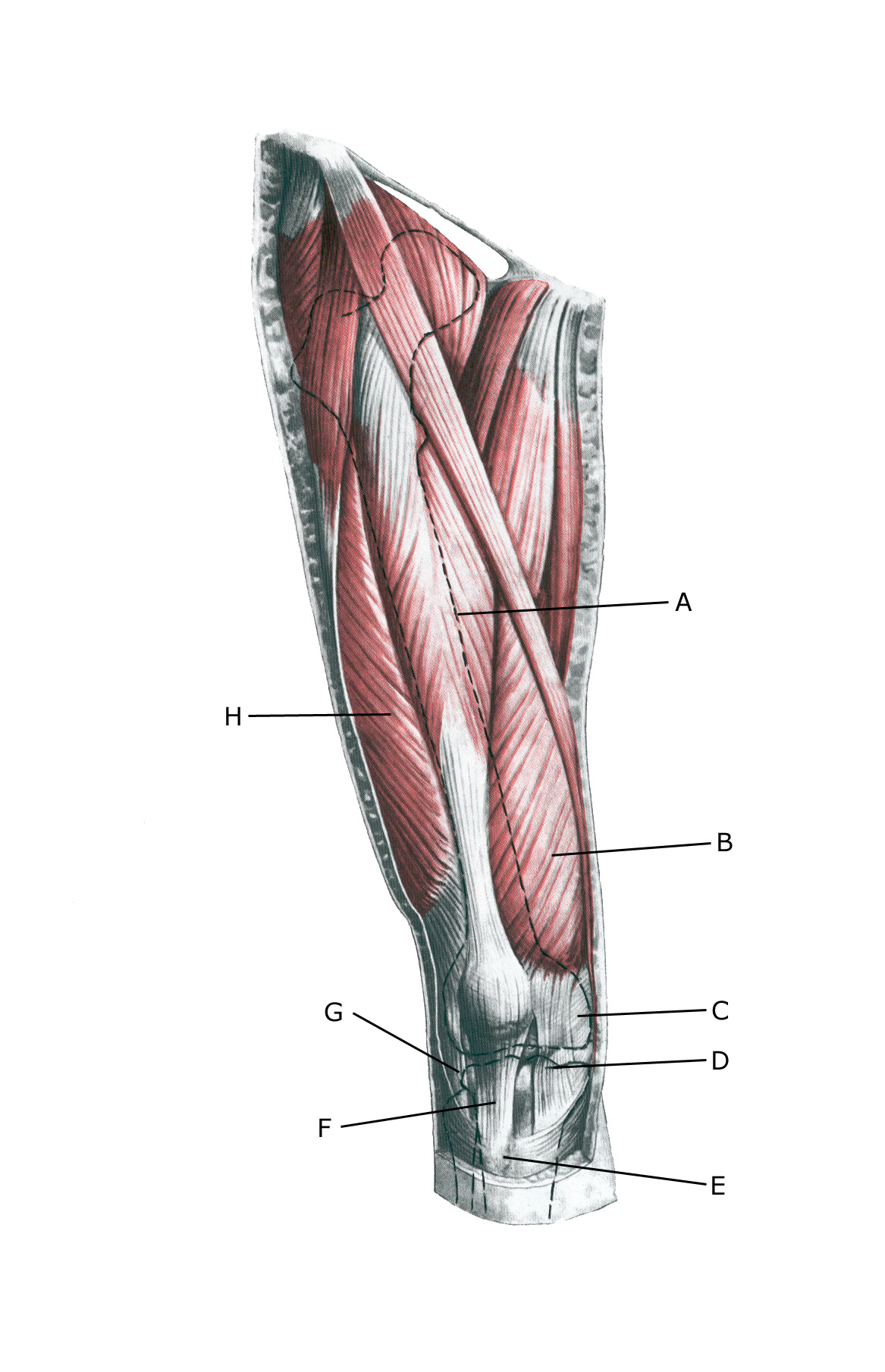 Knee from the front:
Knee from the front:
A. M. rectus femoris
B. M. vastus medialis
C. Retinaculum patellae mediale
D. Retinaculum patellae mediale
E. Tuberositas tibiae
F. Lig. Patellae
G. Retinaculum patellae laterale
H. M. vastus lateralis
Cause
Anterior knee pain is a pain syndrome where the pain cannot be attributed to a recognised condition. Several specific conditions can cause almost the same symptoms, and these conditions must be ruled out in order to diagnose anterior knee pain (PFPS).
Specific diagnoses to rule out include knee cartilage damage, looseness of the kneecap, meniscus lesion, Osgood-Schlatter, Sinding Larsen, anterior cruciate ligament rupture, and fractures and infections. The condition most commonly affects girls.
Symptoms
Strain-related slow-onset pain in the front of the knee. Provoked by running and stair climbing, among other things. Sometimes there may be a sensation of locking of the knee joint (pseudo-locking) and knee failure. The discomfort often lasts for several years, but usually subsides
Examination
Usually, the diagnosis is made by general clinical examination where the specific causes of anterior knee pain are ruled out. Imaging cannot establish the diagnosis of anterior knee pain, but can detect/exclude several of the specific causes.
Treatment
Treatment primarily includes relief from pain-inducing activity (jumping, kicking), balance training, stretching and strengthening of the muscles around the knee (Collins NJ, et al. 2018). Early treatment shortens the course.
Complications
The prognosis is very good, but can be long-lasting. In case of lack of progress, you need to consider
