Anatomy
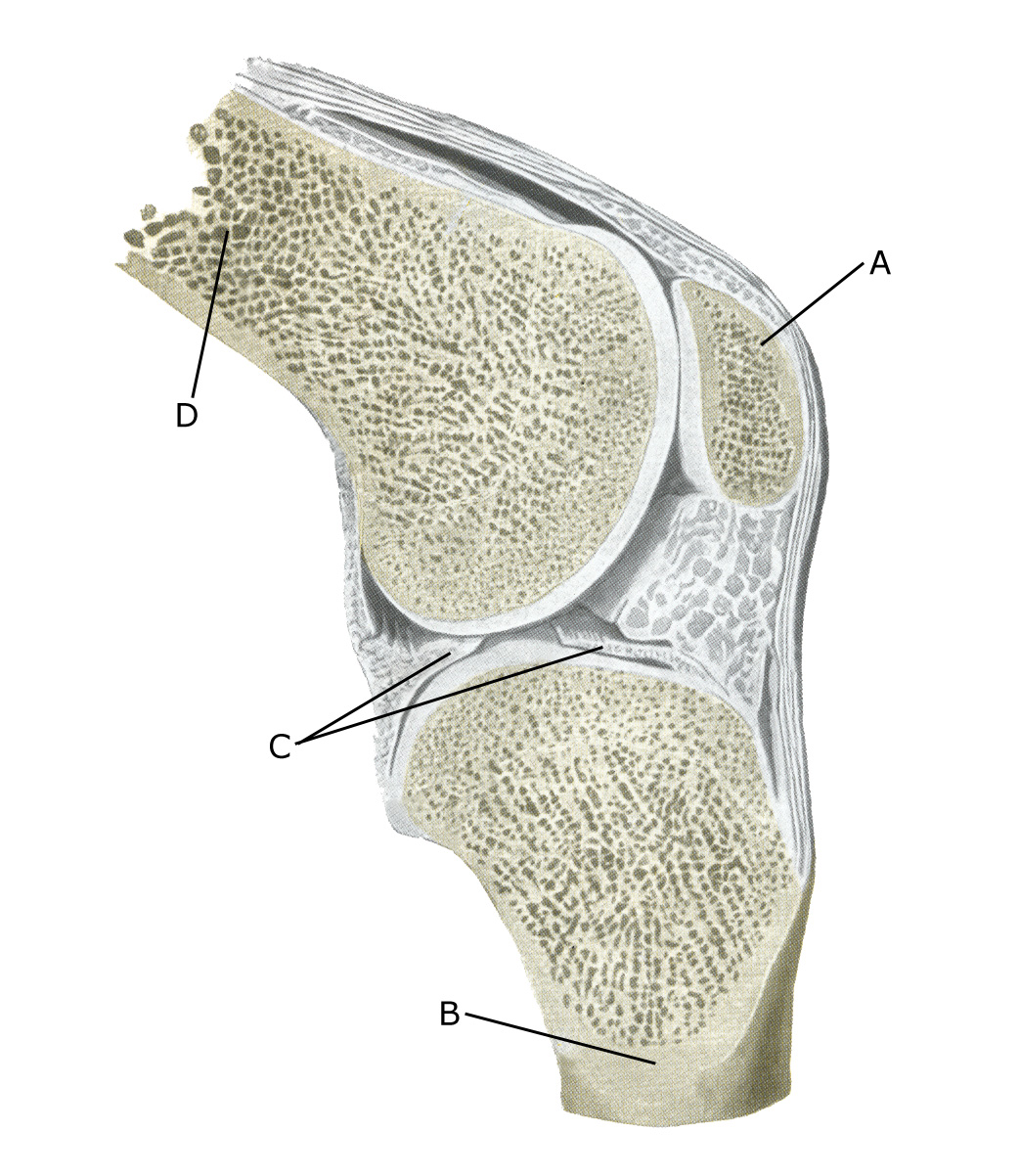 The bones of the knee joint include the femur (thigh bone), tibia (shin bone) and patella (kneecap). The articular surfaces are covered with a few millimetres of cartilage that serves to reduce stress on the articular surfaces. The kneecap slides against the femur when the knee bends and extends.
The bones of the knee joint include the femur (thigh bone), tibia (shin bone) and patella (kneecap). The articular surfaces are covered with a few millimetres of cartilage that serves to reduce stress on the articular surfaces. The kneecap slides against the femur when the knee bends and extends.
Knee joint:
A. Patella (kneecap)
B. Tibiae (Shin bone)
C. Meniscus lateralis (Outer meniscus)
D. Femur (Femur)
Cause
Repeated strain or an acute injury can damage the cartilage and bone beneath the cartilage. The severity of cartilage damage can range from insignificant superficial irregularities in the cartilage to severe symptomatic and treatable cartilage damage where large areas of cartilage are completely missing. The severity of symptoms does not always reflect the severity of the cartilage damage.
Cartilage damage often occurs after twisting the knee, falling on the knee, dislocation of the kneecap or repeated overloading. In children/young people over the age of 10, a piece of cartilage and bone can become loose in the knee (osteochondritis dissecans). A loose piece of cartilage can move around the joint (joint mouse) See ultrasound scan and become trapped (locking).
The synovial membrane can become secondarily inflamed (‘inflamed’) and produce increased amounts of synovial fluid. In many cases, the cause of the cartilage damage is unknown. Cartilage damage in the knee increases the risk of later development of osteoarthritis.
Symptoms
Pain in the joint when moving with strain, e.g. climbing stairs. Stiffness in the knee after prolonged sitting. Sometimes there may be swelling in the joint (synovitis). Long-term discomfort may also be accompanied by constant grinding pain and difficulty starting up.
Examination
Cartilage damage to the back of the kneecap is characterised by pain being triggered when the kneecap is pressed against the femur, causing a rough, jarring sensation. A knee X-ray should be taken in two planes after acute knee injury (usually within 1 week) if any of the following apply: the patient is under 12 years old, cannot walk 4 steps due to pain, pressure tenderness of the patella or fibular head (caput fibulae), the knee cannot bend more than 60°, or there is ligament damage (Pittsburgh knee rules).
If cartilage damage is suspected, it is usually necessary to supplement the clinical medical examination with imaging in the form of an MRI scan. Ultrasound scans can detect many, but not all, cartilage injuries see ultrasound scan. If the diagnosis is in doubt, an arthroscopic examination of the knee (arthroscopy) may be necessary.
Treatment
Treatment in mild cases includes relief from the pain-inducing activities. At the same time, increasing strength training within the pain threshold of the muscles and tendons around the knee is started (Kamat Y, et al. 2021). There is no treatment that can restore the damaged cartilage, which has little ability to heal. In some cases, the cartilage damage is so severe that it requires surgery. Unstable loosening of bone fragments (osteochondritis dissecans) in particular requires rapid diagnosis and surgical treatment (Nammour MA, et al. 2024), after which the majority return to sport.
For localised or more widespread cartilage damage, arthroscopy can try various procedures to promote cartilage healing, but results are generally unsatisfactory. Symptomatic joint mice can be surgically removed. In cases of prolonged, severe fluid accumulation in the knee joint (synovitis), an injection of adrenal cortex hormone into the knee joint can be tried as part of rehabilitation.
Bandage
For cartilage damage on the back of the kneecap, some people have experienced an improvement in discomfort when using a knee brace or kneecap stabilising tape. See tape
Complications
Even after surgery to stabilise loose bone fragments (osteochondritis dissecans), the majority return to sport. If no progress is made, it is necessary to consider whether the diagnosis is correct, which often requires additional imaging or arthroscopy.
In particular, the following should be considered:
- Meniscus lesion
- Outer collateral ligament rupture
- Rupture of the posterior cruciate ligament
- Periosteal avulsion (periosteal avulsion)
- Fluid accumulation in the joint
- Inflamed mucosal fold (plica synovialis)
