Anatomy
The bones of the wrist consist of 8 carpal bones (ossa carpi), which together with the two forearm bones, the ulna and radius, form the wrist. There are also 5 metacarpal bones (ossa metarcarpi) and a total of 14 phalanges.
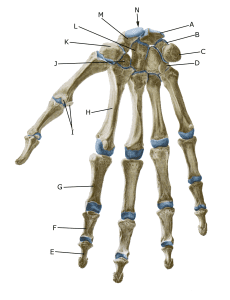 Bones of the right hand palm:
Bones of the right hand palm:
A. Os lunatum
B. Os triquetrum
C. Os pisiforme
D. Os hamatum
E. Phalanx distalis
F. Phalanx media
G. Phalanx proximalis
H. Os metacarpale II
I. Ossa sesamoidea J. Os trapezoideum K. Os trapezium
L. Os capitatum
M. Os scaphoideum
N. Carpus
Right wrist back of hand:

A. Radius
B. Ossa metacarpi I
C. Ossa metacarpi II
D. Ossa metacarpi III
E. Ossa metacarpi IV
F. Ossa metacarpi V
G. Processus styloideus
H. Articulatio radio-ulnaris distalis
I. Ulna
Cause of the problem
Bone fractures can occur as a result of blows or falls. In adults, the forearm bones often fracture close to the wrist, resulting in a characteristic forked angle of the wrist (fractura Colles), which accounts for 1/6 of all fractures in adults.
Among metacarpal bones, special attention should be paid to fractures of the scaphoid bone (os scaphoideum), which is most often overlooked and can cause serious complications with healing due to poor blood supply. Other cases include a fracture of the radius at the elbow (caput radii) combined with a lesion of the ligaments between the two bones of the forearm (membrana interossea) and a dislocation of the joint between the two bones of the forearm at the wrist (Essex-Lopresti lesion). The injury is often overlooked, which can lead to chronic discomfort (Kooistra B et al. 2022)
Symptoms
Sudden onset of forearm pain and painful restriction of movement after a fall, twist or blow. Occasionally, angulation of the forearm or fingers may be seen. In the case of a boat leg fracture, symptoms are often misinterpreted as a ‘sprain’ of the wrist with pain if the hand is bumped (indirect pain).
Delaying treatment of boat bone fractures can cause complications such as delayed healing, non-healing or collapse of the bone (osteonecrosis).
Examination
Sudden onset of severe hand/wrist pain with restricted movement after a fall or impact should lead to urgent medical attention (possibly at a hospital). An X-ray examination can usually reveal the fracture and determine treatment based on the type of fracture.
As not all fractures can be seen on X-ray immediately after the injury, it may be necessary to supplement with an MRI or CT scan or repeat the X-ray after a few weeks. With a fracture of the navicular bone, there is often pressure tenderness close to the joint line on the back of the hand on the thumb side (‘tabatiere’). Pain in both the elbow and wrist should be investigated specifically for Essex-Lopresti lesion.
Treatment
If there is significant displacement or angulation of the bones in the forearm or fingers, the fracture is set in place under anaesthesia and bandaged for a few weeks. In certain types of fractures, it may be necessary to stabilise the fracture surgically (Li NY et al. 2023). It is important to start training the hand as soon as the bandage is removed, which improves mobility and strength (Watt CF et al. 2000).
If the X-ray is normal but a fracture of the scaphoid bone is still suspected, you can apply a stiff bandage and repeat the X-ray after 2 weeks.
Rehabilitation
It is important to maintain fitness and muscle strength of all other muscles while the hand is offloaded. Fitness training in the form of cycling and running can be resumed as soon as it does not aggravate the pain in the fracture. Once the bandage is removed, hand mobility should be maintained.
See rehabilitation under rehabilitation, general. If surgery has been performed, there may be special precautions that the operator will inform you about.
Bandage
It is possible to manufacture customised plastic wrist or finger bandages for use during sports activity after bone fractures.
Complications
In the vast majority of cases, the fracture heals without complications. In some cases, however, there may be poor healing, impaired blood vessel and nerve supply to the arm and possibly musculoskeletal syndrome. If there is a lack of progress or noticeable pain, you should consult your doctor.
