Anatomy
The tibia (shin bone) and fibula (fibula) together with the talus (ankle roll bone) form the bones of the ankle joint. The heel bone (calcaneus) and some of the 7 tarsal bones (ossa tarsi) are closely related to the foot joint. In addition, the bones of the foot include 5 metatarsal bones (ossa metatarsi) and the bones of the toes (phalanx).
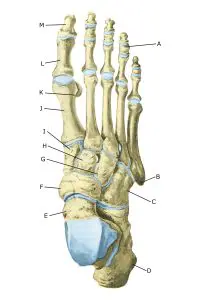 The foot from above:
The foot from above:
A. Phalanx media
B. Tuberositas ossis metatarsalis V
C. Os cuboideum
D. Calcaneus
E. Talus
F. Os naviculare
G. Os cuneiforme laterale
H. Os cuneiforme intermedium
I. Os cuneiforme mediale
J. Os metatarsalei
K. Os sesamoideum
L. Phalanx proximalis
M. Phalanx distalis
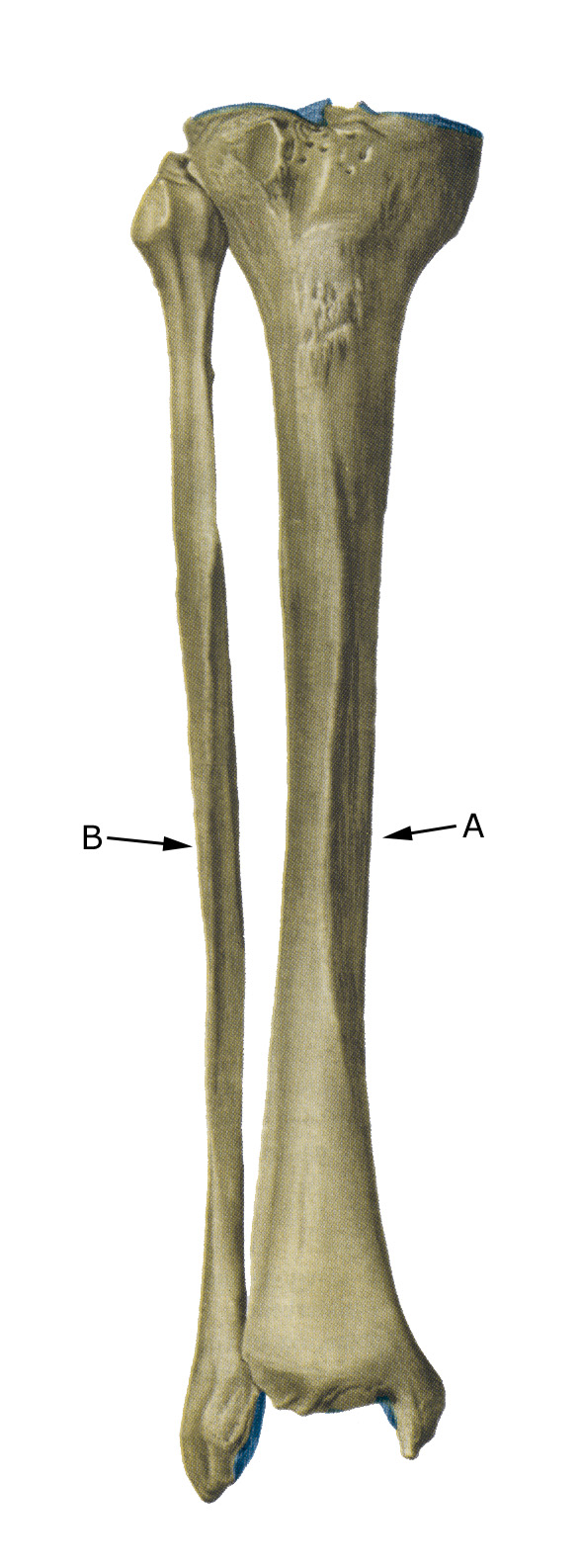 Shinbone from the front
Shinbone from the front
A. Tibia (shinbone)
B. Fibula
Cause of the problem
Repeated overloading of the bones of the ankle, calcaneus, metatarsals and metatarsals that exceeds the strength of the bones can trigger a fatigue fracture (stress fracture), which most often affects the tibia of the inner ankle bone, calcaneus, navicular and metatarsal bones (2nd and 3rd metatarsals, march fracture) (Jungmann PM, Schaeffeler C. 2023).
Eating disorders and lack of menstruation (amenorrhoea) increase the risk of fatigue fractures up to 13 times in teenagers. Low bone mineral density (BMD) increases the risk of fatigue fractures 4.5 times (Nose-Ogura S, et al. 2019).
Symptoms
Increasing pain that worsens with strain (supporting the foot, walking and running). There is pain on pressure (direct and indirect tenderness).
Examination
Suspected fatigue fractures should lead to clinical examination by an appropriate professional who can assess the need for X-ray examination and make a correct diagnosis so that treatment can be started as soon as possible.
X-rays are often normal for the first 2-4 weeks after a fatigue fracture (Koo AY, Tolson DR. 2023). CT, MRI scans (and ultrasound scans) can often diagnose fatigue fractures faster.
Treatment
Treatment depends on which bones are broken. In some cases, offloading without bandaging is chosen, while other foot fatigue fractures require bandaging and, in rare cases, surgery. The healing time for some fatigue fractures (e.g. calcaneus, navicular) is up to six months, but the prognosis is usually good. Good shock-absorbing soles in shoes are recommended.
Until the pain subsides, follow the guidelines under rehabilitation, in general. For fatigue fractures, any eating disorders should of course be treated.
Rehabilitation, specific:
Rehabilitation is entirely dependent on the type of fracture and treatment (conservative or operative). Often it will be possible to maintain cardio and training of all other muscles (guidelines under rehabilitation, general).
If surgery or bandaging has been performed, rehabilitation guidelines should be included from the treatment centre that take into account the type of injury. Generally, the foot should not be loaded until it is pain-free, and it is important that there is a steady progression where the pain decreases despite increasing load.
Complications
If progress is not smooth, you should be reassessed by an appropriate professional to ensure that the fracture is healing as planned. In some cases, a false joint can form (pseudoarthrosis), which will require surgical treatment.
