Anatomy
The various muscles of the abdominal wall are penetrated by the inguinal canal, which contains nerves (N ilioinguinalis and the genital branch of N genitofemoralis) and in men the spermatic cord (funiculus spermaticus). In women, the inguinal canal contains a small fibrous ligament in the 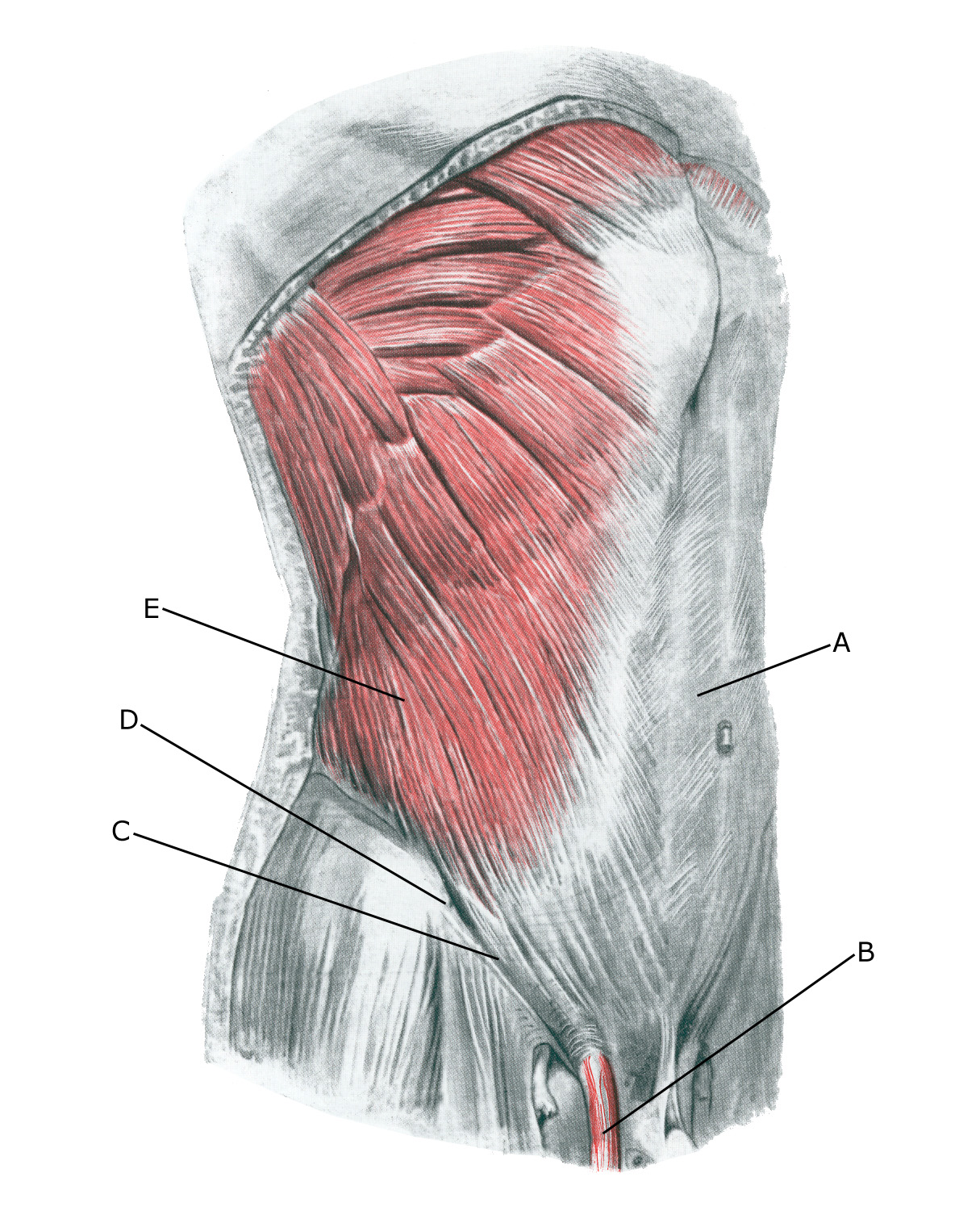 Where the inguinal canal breaks through the abdominal wall, weak spots (anulus inguinalis superficialis and anulus inguinalis profundus) occur.
Where the inguinal canal breaks through the abdominal wall, weak spots (anulus inguinalis superficialis and anulus inguinalis profundus) occur.
The groin channel:
A. M. recti abdominis
B. Funiculus spermaticus
C. Ligamentum inguinale
D. Spina iliaca anterior superior
E. M. obliquus externus abdominis
Right groin channel:
A. Anulus inguinalis superficialis
B. Crus mediale
C. Funiculus spermaticus et m. cremaster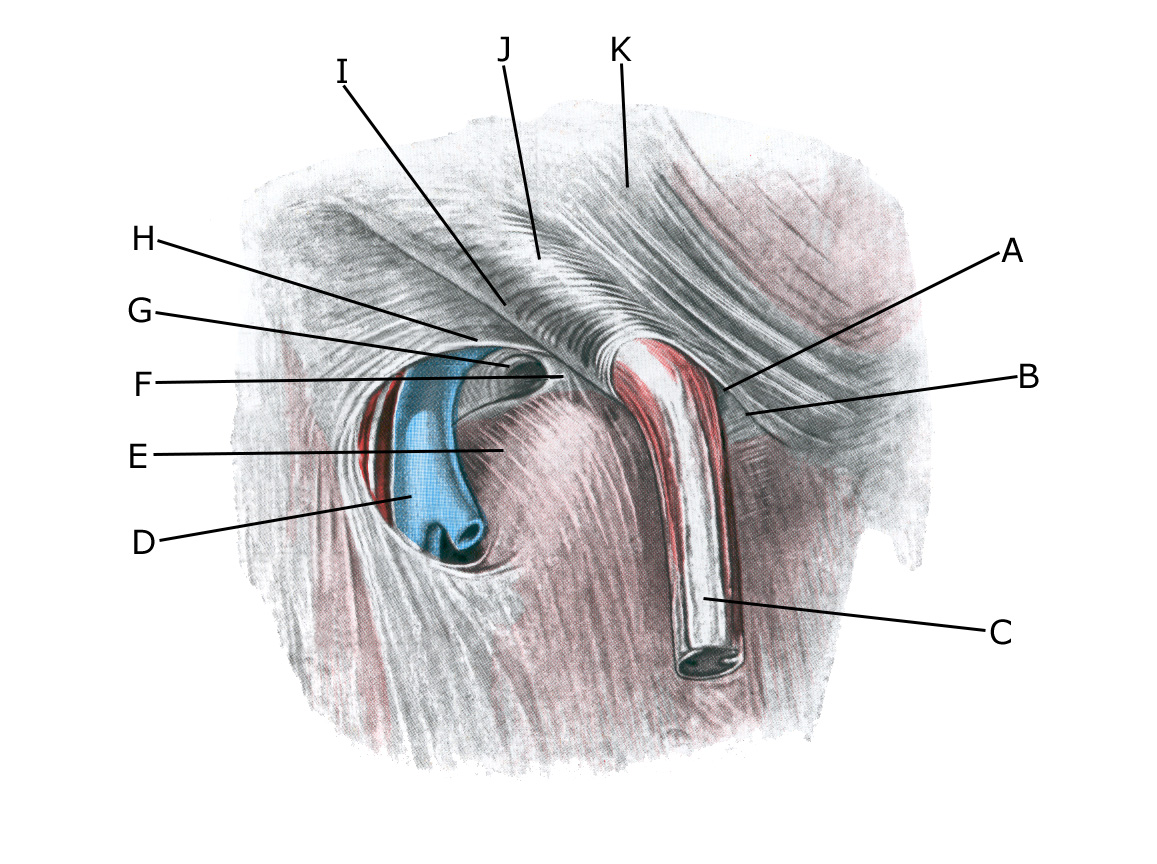 D. V. femoralis
D. V. femoralis
E. Hiatus saphenus
F. Lig. lacunare
G. Anulus femoralis
H. Margo falciformis (cornu superius)
I. Lig inguinale
L. Fibrae intercrurales
K. M. obliquus externus abdominis
Cause
If the abdominal wall becomes too weak, the intestines can be pushed out through the weak spots in the abdominal wall, causing a hernia.
Symptoms
Pain in the groin with aggravation when coughing. Often a filling can be seen in the groin. Usually the bulge (which may contain bowel) can be pressed into place. If the bulge is painful and cannot be pushed into place, the hernia may be trapped (requiring emergency medical attention). There will usually be a lot of pain, vomiting and possibly fever.
Examination
The diagnosis is usually made by a general clinical medical examination. In obvious cases with visible bulging in the groin, the diagnosis is easy. In the absence of inguinal filling, inguinal hernia often becomes a diagnosis of exclusion, where other explanations are ruled out.
If there is any doubt about the diagnosis, an ultrasound or MRI scan can be performed. Ultrasound scans can often detect a hernia when the scan is performed while the patient increases the pressure in the abdominal cavity by pushing (Valsalva manoeuvre).
Treatment
Smaller children and girls are most often operated on, but asymptomatic boys can be observed without surgery. However, there is no full consensus on the indication for surgery in asymptomatic inguinal hernia (Reistrup H, et al. 2023). If the symptoms are mild, you can try abdominal strength training, as it is possible to have an inguinal hernia that does not trigger the current symptoms (Corvatta FA, et al. 2023).
If an incarcerated hernia is suspected, urgent medical attention should be sought to assess the indication for emergency surgery, as there is a risk of permanent damage to the bowel.
Rehabilitation
Usually, sports activity after surgery can be resumed after a few weeks without further rehabilitation. See also general information on rehabilitation in children.
Complications
Before any surgery, you should consider whether the diagnosis is correct.
In particular, the following should be considered:
